Can Statit Qc Software Be Used On Aircraft Repair
Reading time: 23 minutes
Introduction
When you buy a pear, you lot tin instantly evaluate its quality: the size and shape, ripeness, the absence of visible bruising. Only only as yous take the first seize with teeth, will you be able to see if the pear is really that practiced. Fifty-fifty an extremely adept-looking pear might gustatory modality sour or have a worm in it.
The same applies to well-nigh any product, be it a physical object or a slice of software. A website you lot find on the Internet might seem fine at first, but every bit you whorl down, become to another page, or effort to transport a contact request, it can start showing some pattern flaws and errors.
This makes quality command so of import in every field, where an end-user product is created. Even so, a sour pear won't cause as much impairment every bit a self-driving machine with poor quality autopilot software. A single error in an EHR system might put a patient'southward life at risk, while an eCommerce website that has performance issues might toll the possessor millions of dollars in acquirement.
That is why nosotros at AltexSoft put a premium on the quality of software we build for our clients. In this paper, we volition share our insights on the quality assurance and testing process, our best practices and preferred strategies.
1. The Concept of Software Quality: Quality Assurance (QA), Quality Command (QC) and Testing
While to err is human, sometimes the cost of a mistake might be simply too high. History knows many examples of situations when software flaws have caused billions of dollars in waste material or even lead to casualties: from Starbucks coffee shops existence forced to requite away free drinks because of a register malfunction, to the F-35 military aircraft being unable to discover the targets correctly considering of a radar failure.
Lookout the video to learn what events triggered the development of software testing and how it has evolved through the years
In order to make sure the released software is condom and functions as expected, the concept of software quality was introduced. It is often divers as "the caste of conformance to explicit or implicit requirements and expectations". These so-chosen explicit and implicit expectations correspond to the ii basic levels of software quality:
- Functional – the product's compliance with functional (explicit) requirements and design specifications. This attribute focuses on the practical utilise of software, from the indicate of view of the user: its features, performance, ease of use, absence of defects.
- Non-Functional – system's inner characteristics and architecture, i.e. structural (implicit) requirements. This includes the code maintainability, understandability, efficiency, and security.
The structural quality of the software is ordinarily hard to manage: It relies more often than not on the expertise of the engineering squad and can be assured through code review, analysis and refactoring. At the same time, functional aspect can exist bodacious through a set of defended quality direction activities, which includes quality assurance, quality control, and testing.
Oft used interchangeably, the three terms refer to slightly unlike aspects of software quality management. Despite a common goal of delivering a product of the all-time possible quality, both structurally and functionally, they utilize different approaches to this job.
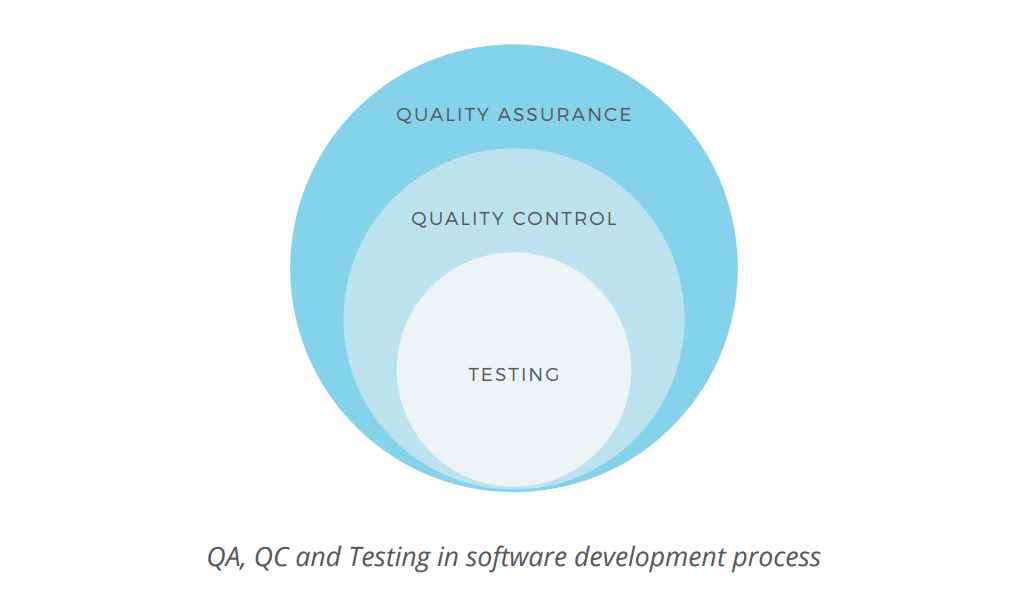
Quality Assurance is a wide term, explained on the Google Testing Blog every bit "the continuous and consistent comeback and maintenance of process that enables the QC job". As follows from the definition, QA focuses more on organizational aspects of quality management, monitoring the consistency of the production process.
Through Quality Control the team verifies the production'due south compliance with the functional requirements. As defined by Investopedia, it is a "procedure through which a concern seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved and manufacturing errors are reduced or eliminated". This action is applied to the finished production and performed before the product release. In terms of manufacturing industry, it is similar to pulling a random particular from an assembly line to see if it complies with the technical specs.
Testing is the basic action aimed at detecting and solving technical issues in the software source code and assessing the overall product usability, performance, security, and compatibility. It has a very narrow focus and is performed past the exam engineers in parallel with the development process or at the dedicated testing stage (depending on the methodological approach to the software development cycle).
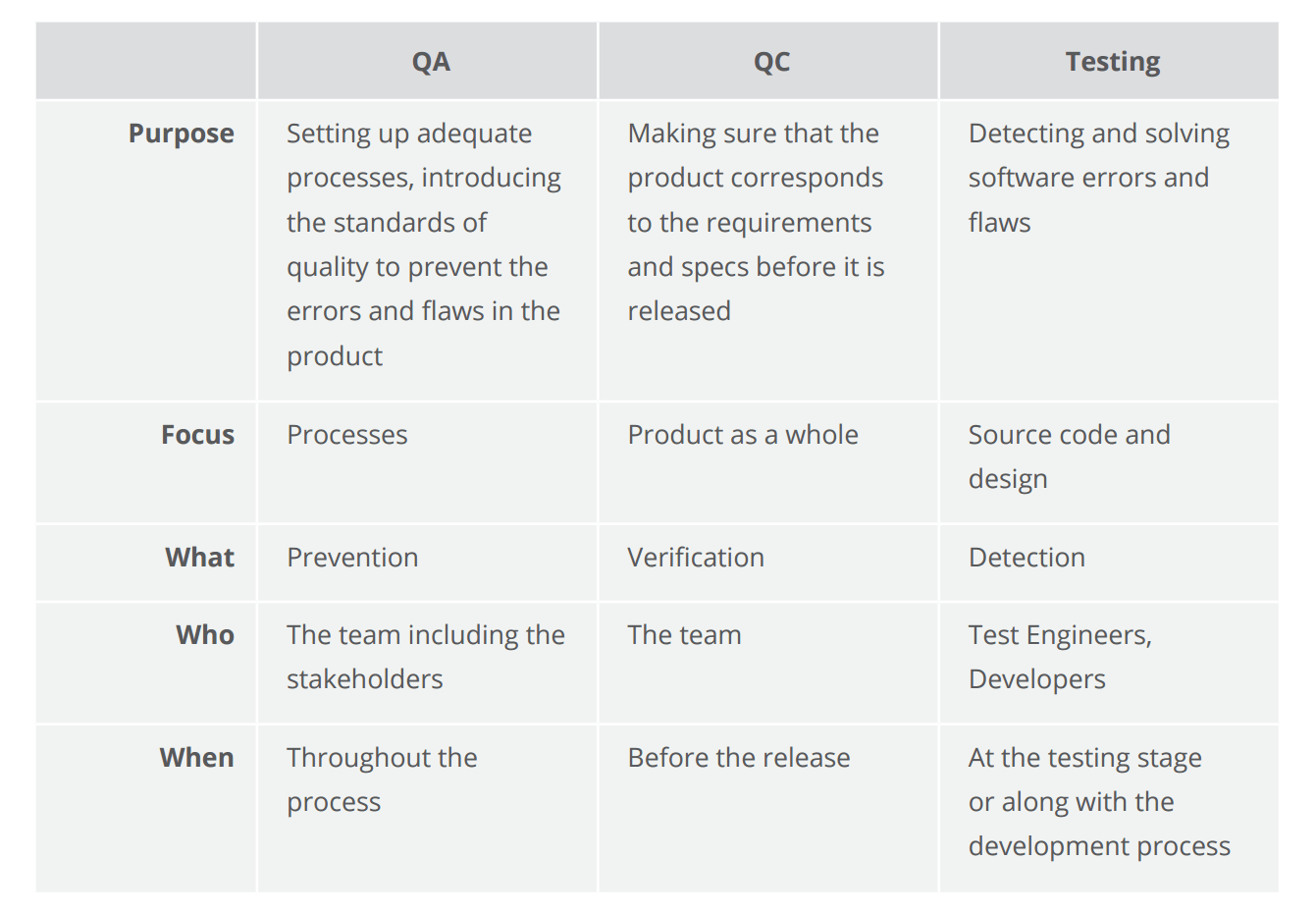
The concepts of quality assurance, quality command, and testing compared
If applied to the process of car manufacturing, having a proper quality assurance process means that every squad fellow member understands the requirements and performs his/her piece of work co-ordinate to the normally accepted guidelines. Namely, information technology is used to make sure that every single action is performed in the right order, every item is properly implemented and the overall processes are consistent and then that nothing can crusade a negative impact on the terminate product.
Quality command tin can be compared to having a senior manager walk into a production department and pick a random car for an examination and test drive. Testing activities, in this case, refer to the process of checking every joint, every mechanism separately, also as the whole product, whether manually or automatically, conducting crash tests, operation tests, and bodily or simulated exam drives.
Due to its hands-on approach, software testing activities remain a discipline of heated discussion. That is why we will focus primarily on this aspect of software quality management in this paper. Just before we go into the details, permit's define the main principles of software testing.
2. The Main Principles of Software Testing
Formulated over the past 40 years, the 7 principles of software testing represent the ground rules for the process. These are:
Testing shows presence of mistakes.Testing is aimed at detecting the defects within a slice of software. Merely no matter how thoroughly the product is tested, we can never be 100 percent sure that there are no defects. We can only utilise testing to reduce the number of unfound issues.
Exhaustive testing is impossible.There is no way to test all combinations of data inputs, scenarios, and preconditions within an awarding. For example, if a single app screen contains ten input fields with 3 possible value options each, this means to cover all possible combinations, test engineers would need to create 59,049 (310) test scenarios. And what if the app contains 50+ of such screens? In guild not to spend weeks creating millions of such less possible scenarios, information technology is improve to focus on potentially more significant ones.
Early testing.As mentioned in a higher place, the cost of an error grows exponentially throughout the stages of the SDLC. Therefore it is of import to start testing the software equally soon equally possible so that the detected issues are resolved and do non snowball.
Defect clustering.This principle is often referred to every bit an application of the Pareto principle to software testing. This means that approximately 80 percent of all errors are usually constitute in merely 20 percent of the system modules. Therefore, if a defect is found in a particular module of a software program, the chances are there might exist other defects. That is why it makes sense to test that area of the product thoroughly.
Pesticide paradox.Running the same prepare of tests again and again won't help yous find more than issues. As soon as the detected errors are fixed, these test scenarios get useless. Therefore, information technology is important to review and update the tests regularly in club to adapt and potentially discover more than errors.
Testing is context dependent.Depending on their purpose or industry, unlike applications should be tested differently. While safety could exist of primary importance for a fintech production, it is less of import for a corporate website. The latter, in its turn, puts an emphasis on usability and speed.
Absenteeism-of-errors fallacy.The complete absenteeism of errors in your product does not necessarily mean its success. No affair how much fourth dimension you lot accept spent polishing your code or improving the functionality if your product is not useful or does not meet the user expectations it won't exist adopted by the target audience.
While the in a higher place-listed principles are undisputed guidelines for every software testing professional, there are more aspects to consider. Some sources note other principles in improver to the bones ones:
- Testing must exist an independent process handled by unbiased professionals.
- Test for invalid and unexpected input values besides as valid and expected ones.
- Testing should be performed only on a static piece of software (no changes should exist made in the procedure of testing).
- Utilise exhaustive and comprehensive documentation to define the expected test results.
3. The Role of Testing in Software Evolution Life Bicycle
3.i. Waterfall Model
Representing a traditional software development life cycle, the Waterfall model includes six consecutive phases: planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance.
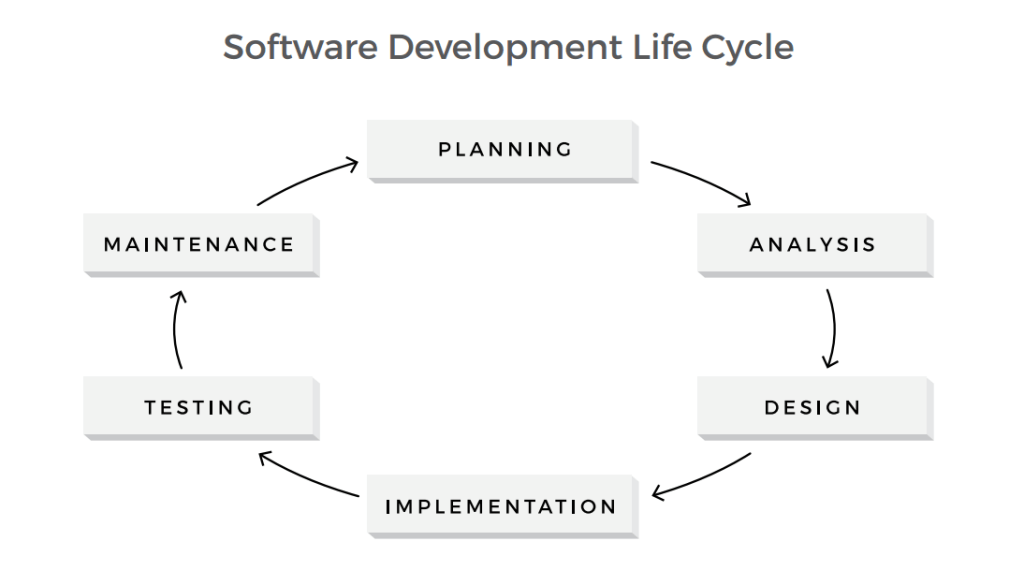
SDLC Waterfall Model
In the testing stage a product, already designed and coded, is existence thoroughly tested before the release. However, the practice shows that software errors and defects detected at this stage might be besides expensive to fix, as the cost of an error tends to increment throughout the software development process.
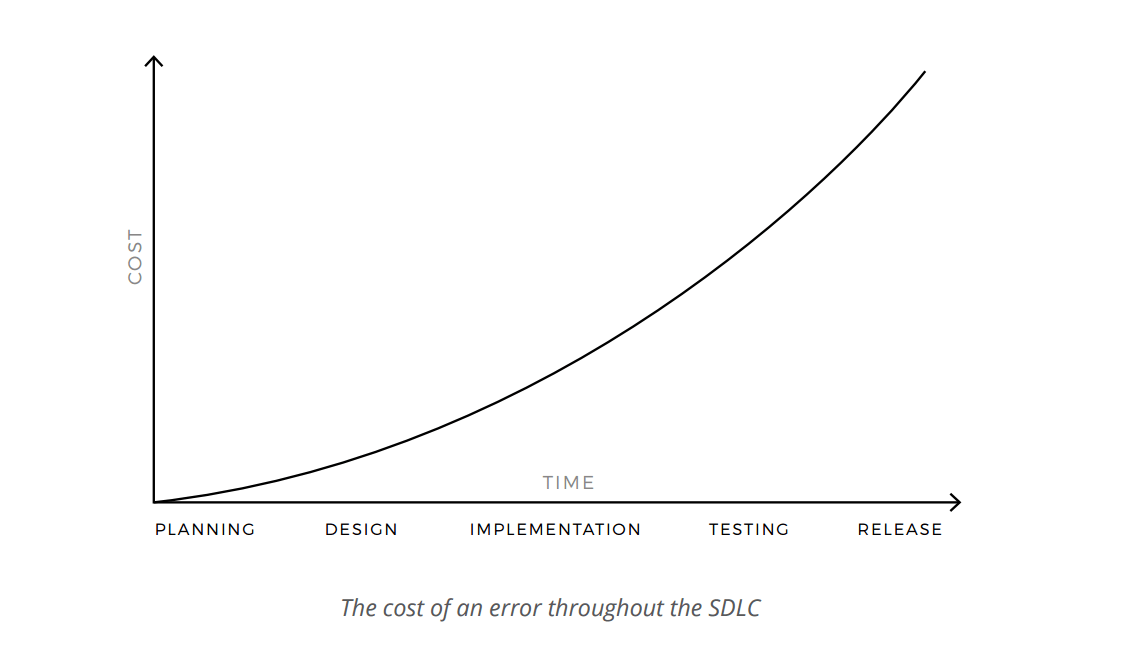
For instance, if there is an mistake in the specifications, detecting it early in the planning stage wouldn't cause significant losses to your business concern. However, the damage grows exponentially throughout the further stages of the process. If such an fault is detected at the design stage, y'all will need to rework your designs to fix it. But if you aren't able to detect the mistake before the production is built, you might demand to make some major changes to the design too as the source code. This volition require a significant amount of effort and investment.
The aforementioned is the case for errors produced in the process of implementation. If a characteristic has a flaw in its logic, building more functionality on top of information technology might cause a serious damage in the long run. Therefore, information technology is better to test every characteristic while the product is still being congenital. This is where iterative Agile methods prove benign.
3.2. Agile Testing
Being an integral role of the software development process, Agile breaks the evolution process into smaller parts, iterations, and sprints. This allows testers to piece of work in parallel with the residuum of the squad throughout the process and fix the flaws and errors immediately after they occur.
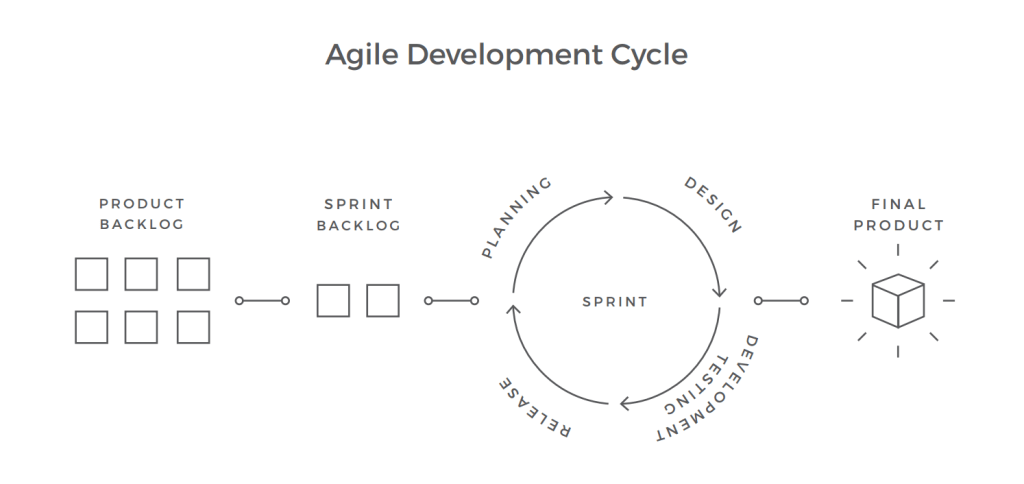
The master purpose of such procedure is to deliver new software features fast and with the best quality. Therefore, this arroyo is less cost-intensive: Fixing the errors early in the development process, before more bug snowball, is significantly cheaper and requires less effort. Moreover, efficient communication within the team and active involvement of the stakeholders speeds up the process and allows for ameliorate-informed decisions. Y'all can find out more than about roles and responsibilities in a testing team in our defended article.
The Active testing approach is more almost building up a QA practice equally opposed to having a QA squad. Amir Ghahrai, a Senior Test Consultant at Amido, comments on this matter: "Past amalgam a QA squad, we fall in the danger of separating the testers from vital conversations with the product owners, developers, etc. In Agile projects, QA should exist embedded in the scrum teams because testing and quality is not an afterthought. Quality should be baked in right from the kickoff."
3.3. DevOps Testing
For those who take Agile experience, DevOps gradually becomes a common practice. This new software development methodology requires a high level of coordination betwixt various functions of the deliverable chain, namely development, QA, and operations.
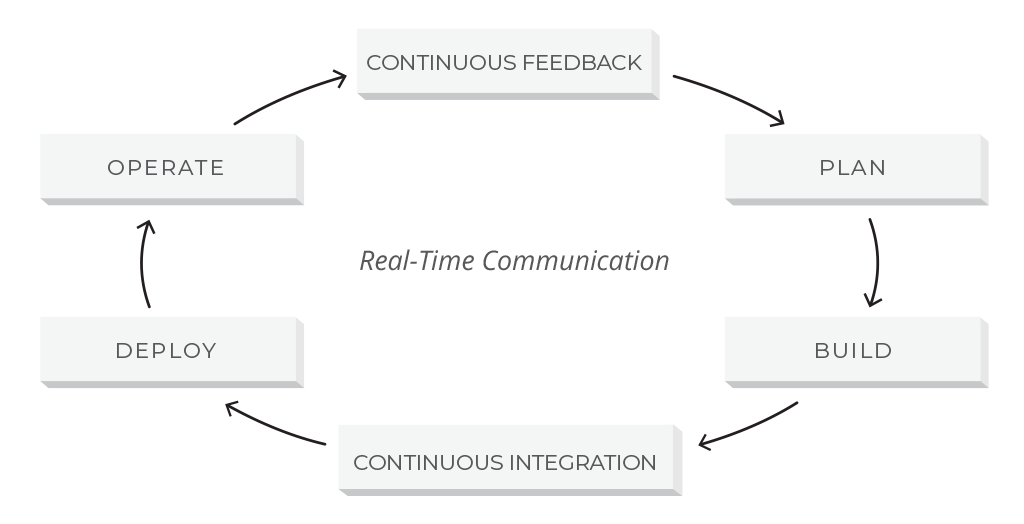
A DevOps lifecycle
DevOps is ofttimes referred to equally an extension of Agile that bridges the gap between evolution along with QA and operations. However, unlike Agile, DevOps includes the concept of continuous development where the code, written and committed to version control, will be built, deployed, tested and installed in the production environment that is ready to be consumed by the end-user. DevOps places a keen accent on automation and continuous integration tools that let for the high-velocity commitment of applications and services.
The fact that testing takes place at each stage in the DevOps model changes the role of testers and the overall idea of testing. Therefore, to be able to finer behave out testing activities, testers are now expected to take technical skills and even be lawmaking savvy.
According to the PractiTest survey, the Active trend is an undisputed leader, while almost xc per centum of respondents work at least in some Agile projects within their organizations. That said, a third of the respondents is however applying the Waterfall model in some projects, following a steady decrease in the employ of that method. DevOps keeps growing, merely slower than before.
four. The Process of Software Testing in Practice
Organizing a software testing procedure can exist quite challenging. Nosotros at AltexSoft follow the iii major steps in the software testing process: planning, execution, and reporting.
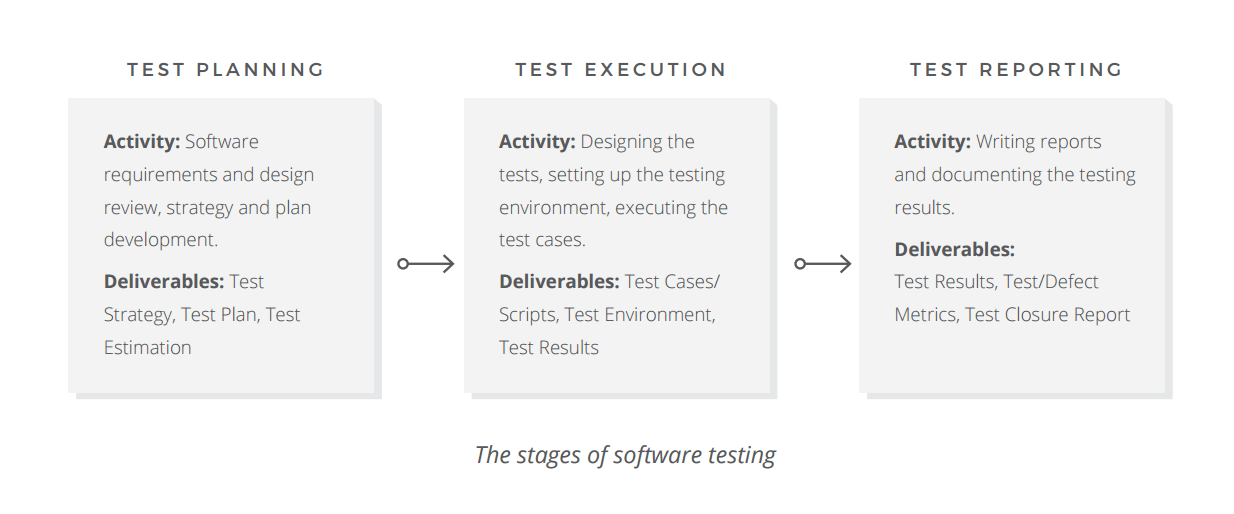
4.ane. Exam Planning: Artifacts and Strategy
As whatever other formal process, testing activities are typically preceded by thorough preparations and planning. The main goal of this stage is to make sure the squad understands the customer objectives, the principal purpose of the product, the possible risks they need to address, and the outcomes they expect to attain. 1 of the documents created at this phase, the mission or assignment of testing, serves to solve this task. It helps align the testing activities with the overall purpose of the product and coordinates the testing effort with the residue of the team's piece of work.
Roger S. Pressman, a professional person software engineer, famous author, and consultant, states: "Strategy for software testing provides a roadmap that describes the steps to be conducted as role of testing, when these steps are planned and then undertaken, and how much endeavour, fourth dimension, and resource will be required."
Also referred to as examination approach or compages, exam strategy is another antiquity of the planning stage. James Bach, a testing guru who created the Rapid Software Testing course, identifies the purpose of a test strategy as "to clarify the major tasks and challenges of the exam project." A good test strategy, in his opinion, is product specific, applied and justified.
Depending on when exactly in the procedure they are used, the strategies can exist classified as preventive or reactive. In add-on to that, at that place are several types of strategies, that can exist used separately or in conjunction:
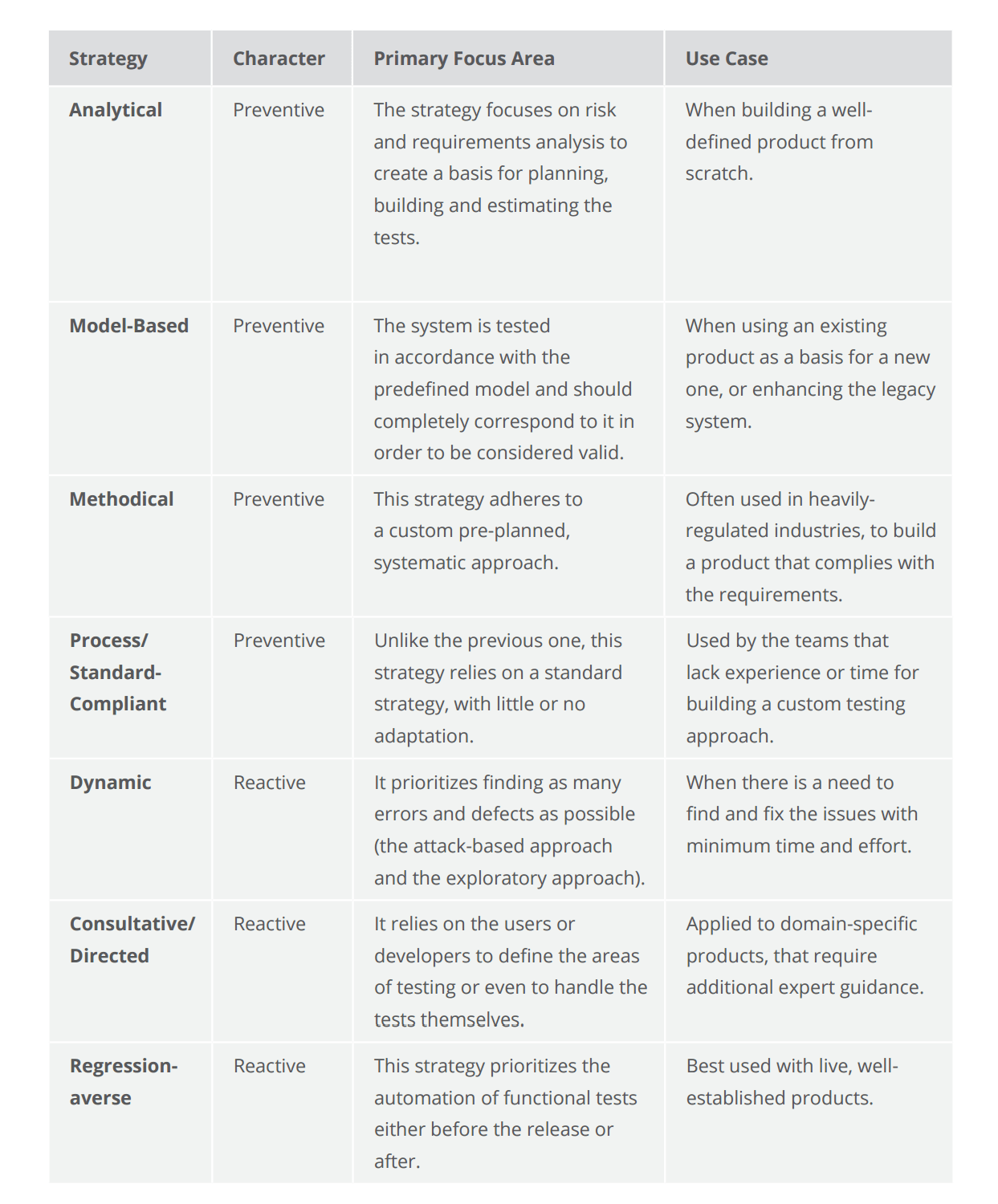
The seven types of test strategies
While a test strategy is a high-level document, exam plan has a more hands-on arroyo, describing in detail what to examination, how to test, when to test and who will do the test. Dissimilar the static strategy document, that refers to a project as a whole, test plan covers every testing stage separately and is ofttimes updated by the projection director throughout the procedure.
According to the IEEE standard for software test documentation, a test plan certificate should contain the following data:
- Test plan identifier
- Introduction
- References (list of related documents)
- Exam items (the product and its versions)
- Features to exist tested
- Features not to be tested
- Item pass or fail criteria
- Exam approach (testing levels, types, techniques)
- Intermission criteria
- Deliverables (Test Programme (this document itself), Test Cases, Test Scripts, Defect/Enhancement Logs, Examination Reports)
- Test surround (hardware, software, tools)
- Estimates
- Schedule
- Staffing and training needs
- Responsibilities
- Risks
- Assumptions and Dependencies
- Approvals
Writing a plan, which includes all of the listed information, is a fourth dimension-consuming task. In agile methodologies, with their focus on the product instead of documents, such a waste of time seems insufficient.
To solve this trouble, James Whittaker, a Technical Evangelist at Microsoft and former Engineering Managing director at Google, introduced The ten Minute Test Program approach. The primary thought behind the concept is to focus on the essentials commencement, cutting all the fluff by using elementary lists and tables instead of large paragraphs of detailed descriptions. While the 10-minute timebox seems a little bit unrealistic (None of the teams in the original experiment was able to meet this requirement), the idea of reducing and limiting the planning time itself is highly reasonable. Equally a outcome, 80 per centum of the planning can be finished inside only thirty minutes.
4.ii. Pattern and Execution
As a starting signal for the test execution, nosotros need to define what is subject area to testing. In social club to answer this question, QA teams develop test cases. In a nutshell, a test case describes the preconditions, desired outcomes, and postconditions of a specific exam scenario, aimed at verifying that a characteristic meets the basic requirements.
The adjacent step in test execution is setting up the testing environs. The chief criteria for this function are to make certain that the testing environment is as close to the cease user'due south actual surround (hardware and software) every bit possible. For example, a typical examination environment for a spider web application should include Spider web Server, database, OS, and browser.
The software testing procedure identifies two broad categories: static testing and dynamic testing.
Static testing initially examines the source code and software project documents to catch and prevent defects early in the software testing life cycle. Also called non-execution technique or verification testing, static testing could be performed every bit inspections, breezy and technical reviews, or reviews during walkthrough meetings. Informal review is a inexpensive testing variant that a QA analyst can conduct anytime during the project. Inspection, also called a formal review, is planned and controlled past the moderator. During the review meeting, errors establish by QA analysts are discussed and documented in the review written report.
Equally before long every bit the principal preparations are finished, the squad gain with dynamic testing where software is tested during execution. This whitepaper has the most focus on the dynamic testing process equally a practical and most commonly used fashion to validate code behavior. Dynamic testing can be described by methods, levels, and types of underlying QA activities. Let'due south have a closer look at this segment of the dynamic testing procedure.
Software testing methods are the ways the tests are conducted. They include black box testing, white box testing, greyness box testing, and advertizement hoc testing.
Software testing levels describe stages of software development when testing is conducted. That said, at that place are 4 progressive testing levels based on the area they focus on the software evolution process: unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user credence testing (UAT).
Software testing types are the approaches and techniques that are applied at a given level using an appropriate method to address the examination requirements in the most efficient way. They are vast in number while serving different objectives.
To sum upwardly, you lot can do apply case testing (a type) during organization or acceptance testing (a level) using black box testing (a method).
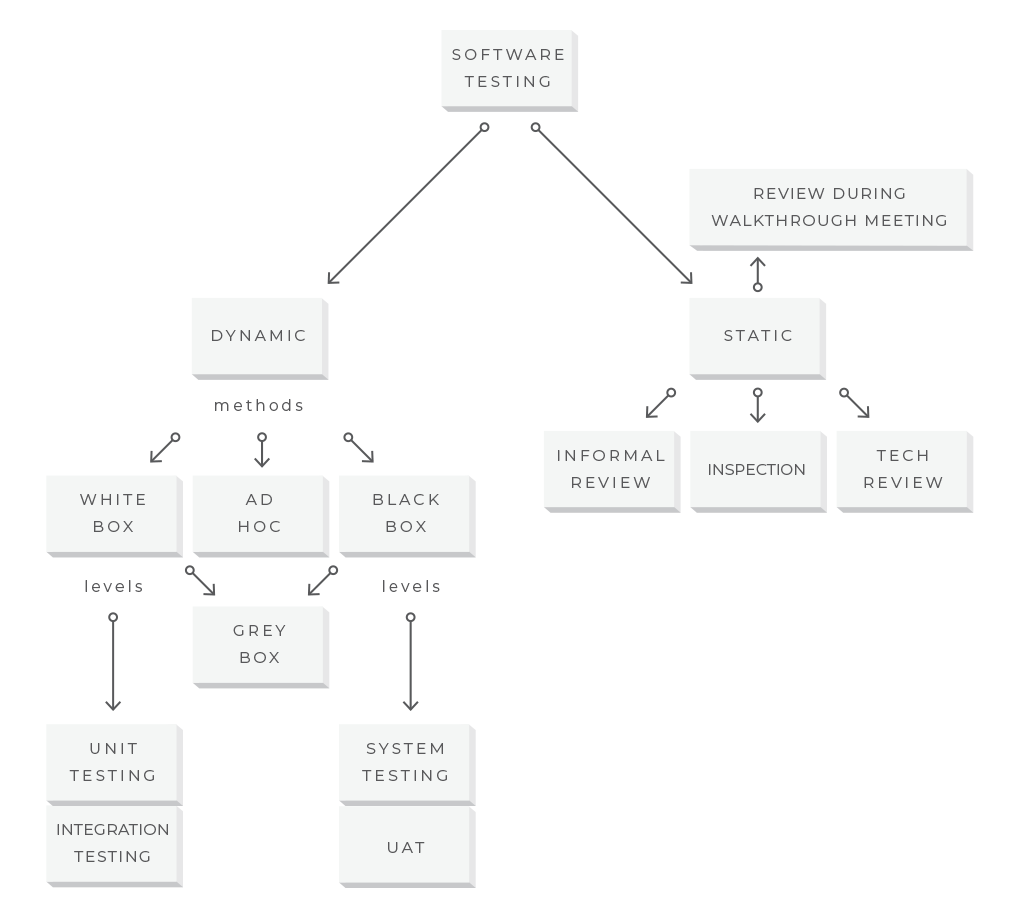
The software testing process segmentation: static and dynamic testing
4.three. Documentation and Reporting
As there is no perfect software, the testing is never 100 percentage complete. Information technology is an ongoing process. However, at that place exist the so-called "go out criteria", which define whether there was "enough testing" conducted, based on the risk assessment of the project.
At that place are common points that are present mostly in leave criteria:
- Examination instance execution is 100 percent complete.
- A system has no high priority defects.
- Performance of the organisation is stable regardless of the introduction of new features.
- The software supports all necessary platforms and/or browsers
- User acceptance testing is completed.
As before long every bit all of these criteria (or any custom criteria that y'all have gear up in your project) are met, the testing comes to its closure.
The testing logs and status reports are documented throughout the process of the test execution. Every issue establish in the product should exist reported and handled accordingly. The test summary and test closure reports are prepared and provided to the stakeholders. The team holds a retrospective coming together in order to ascertain and document the bug that occurred during the development and better the process.
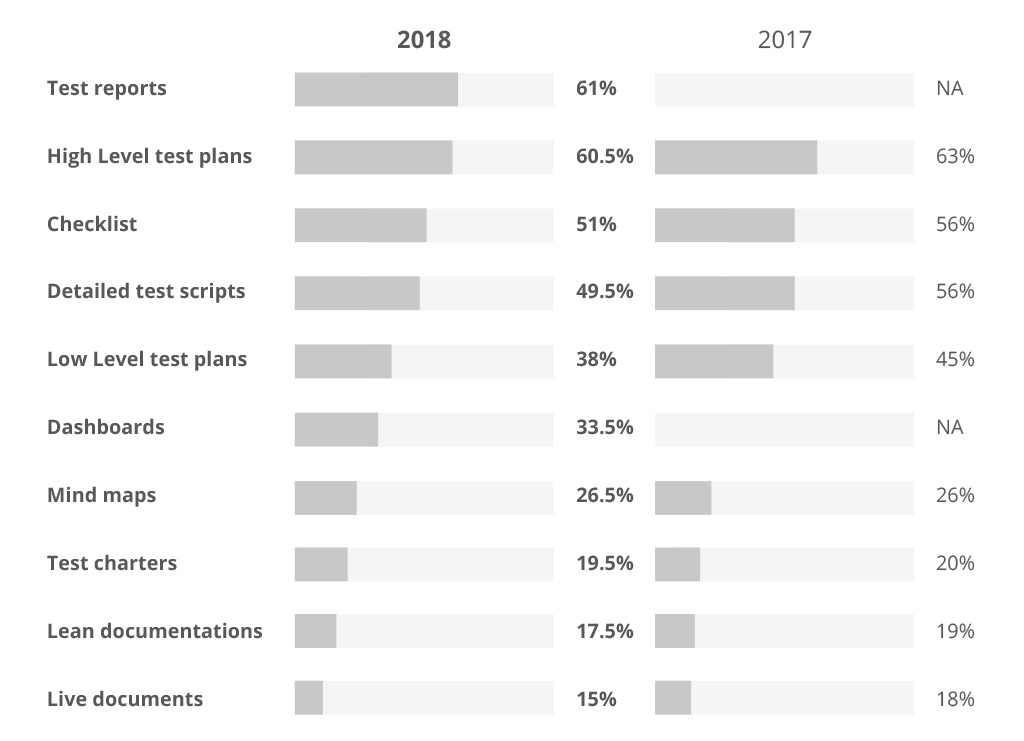
PractiTest Testing documentation survey. From the STATE OF TESTING Study 2022
Co-ordinate to the survey conducted by PractiTest, an end-to-end QA and test direction solution, there is a constant decrease in the corporeality of formal testing documentation written. This tendency signals the demand to streamline testing all across the manufacture.
v. The Levels of Software Testing
A slice of software is more than several lines of code. It is usually a multilayer, complex arrangement, incorporating dozens of split up functional components and tertiary-party integrations. Therefore, efficient software testing should go far across but finding errors in the source code. Typically, the testing covers the post-obit levels of software.
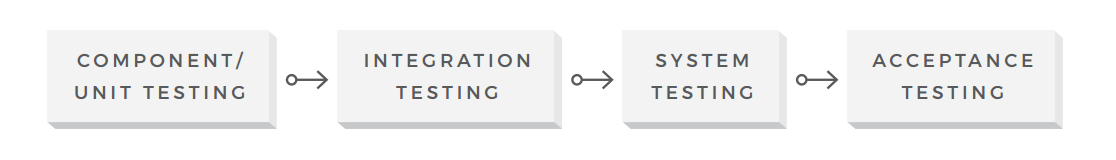
The levels of software testing
- Component/Unit Testing
The smallest testable part of the software system is often referred to as a unit. Therefore, this testing level is aimed at examining every single unit of measurement of a software system in order to make sure that information technology meets the original requirements and functions as expected. Unit testing is commonly performed early on in the development process past the engineers themselves, not the testing team.
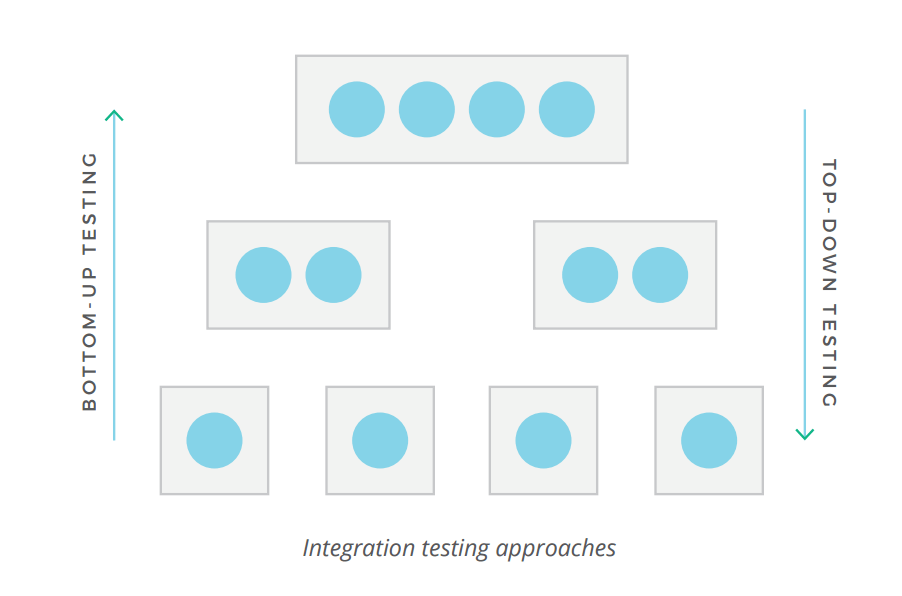
- Integration Testing
The objective of the adjacent testing level is to verify whether the combined units work well together as a group. Integration testing is aimed at detecting the flaws in the interactions between the units within a module. There are two primary approaches to this testing: bottom-up and pinnacle-down methods. The bottom-upwardly integration testing starts with unit tests, successively increasing the complexity of the software modules under examination. The height-down method takes the opposite arroyo, focusing on loftier-level combinations get-go and examining the simple ones after.
- Arrangement Testing
At this level, a complete software system is tested equally a whole. This stage serves to verify the product's compliance with the functional and technical requirements and overall quality standards. System testing should exist performed by a highly professional testing team in an environment as close to the real business apply scenario as possible.
- User Acceptance Testing
This is the last stage of the testing process, where the product is validated confronting the end user requirements and for accuracy. This final step helps the team decide if the production is ready to be shipped or not. While small problems should be detected and resolved earlier in the procedure, this testing level focuses on overall system quality, from content and UI to performance issues. The acceptance stage might be followed by an blastoff and beta testing, allowing a minor number of actual users to endeavour out the software earlier it is officially released.
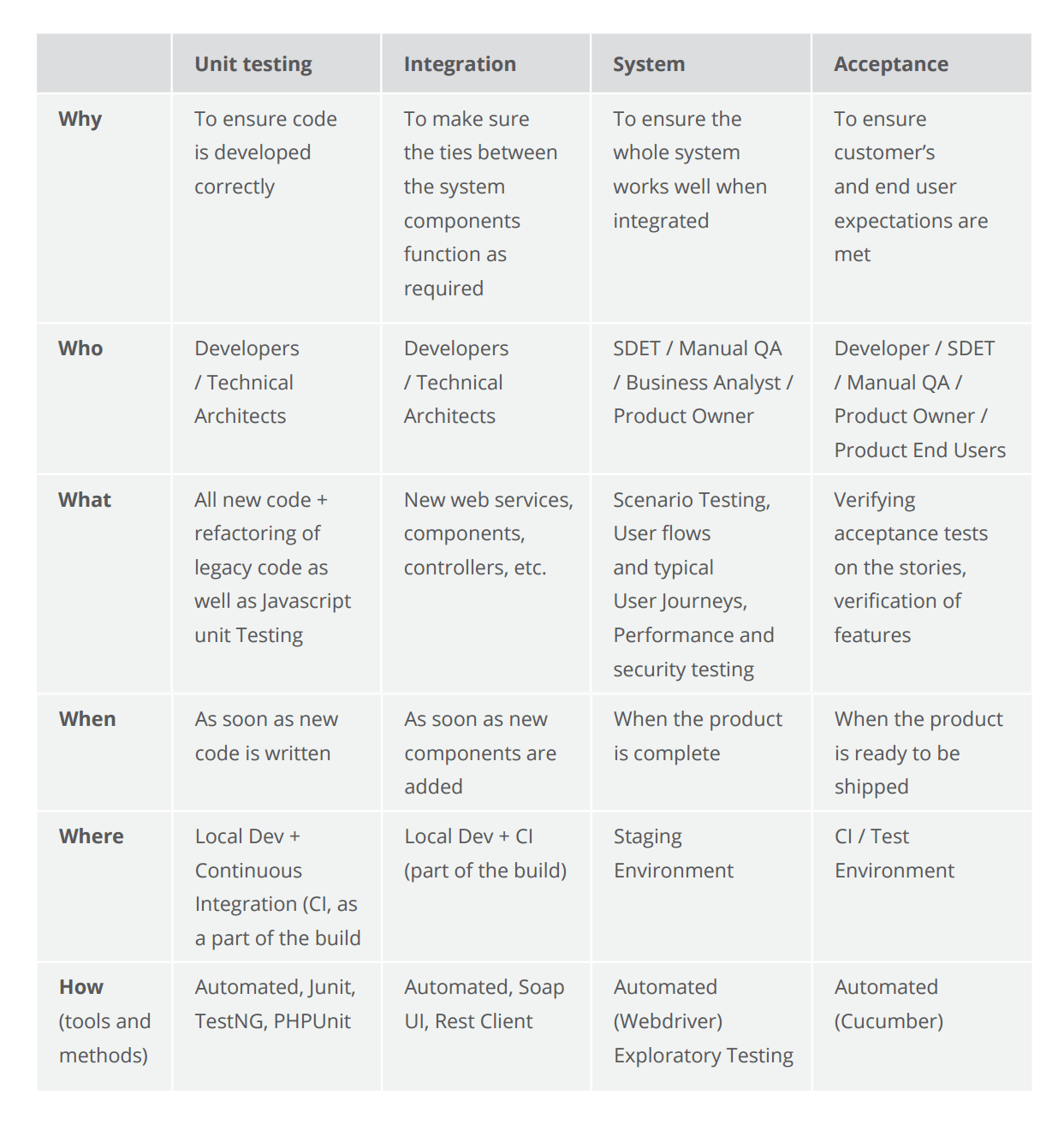
The levels of software testing compared
In Agile software development, the testing typically represents an iterative process. While the levels by and large refer to the complete product, they can also be applied to every added characteristic. In this example, every small unit of the new functionality is being verified. Then the engineers check the interconnections between these units, the way the feature integrates with the rest of the system and if the new update is set to be shipped.
6. The Methods of Software Testing
- Black Box Testing
This method gets its proper noun because a QA engineer focuses on the inputs and the expected outputs without knowing how the application works internally and how these inputs are candy. The purpose of this method is to check the functionality of the software making certain that it works correctly and meets user demands. This method can exist applied to any testing level merely is used mostly for organisation and user acceptance testing.
 A QA specialist doesn't consider the internal processes of the production while conducting a test
A QA specialist doesn't consider the internal processes of the production while conducting a test
- White Box Testing
Unlike black box testing, this method requires profound noesis of the code every bit it entails testing of some structural part of the application. Therefore, generally, the developers straight involved in writing code are responsible for this blazon of testing. The purpose of white box testing is to heighten security, the flow of inputs/outputs through the application, and to ameliorate design and usability. This method is mainly used at the unit and integration testing levels.
- Grayness Box Testing
This method is a combination of the previous ii, since it involves testing of both functional and structural parts of the application. Using this method, an experienced tester has fractional noesis of the internal application construction and based on this knowledge tin design test cases while still testing from the black-box perspective. This method is mostly applicable to the integration testing level.
- Ad Hoc Testing
This is an informal testing method equally it'southward performed without planning and documentation. Conducting tests informally and randomly without whatever formal, expected results, the tester improvises the steps and arbitrarily executes them. Though defects found with this method are more difficult to reproduce given the absence of written examination cases, this approach helps find important defects chop-chop, something which cannot be done with formal methods.
7. The Types of Software Testing
Based on the main objective of the process, testing can exist of different types.
Based on the chief objective of the process, testing tin can exist of different types. Here are the nearly popular testing types according to the ISTQB survey.
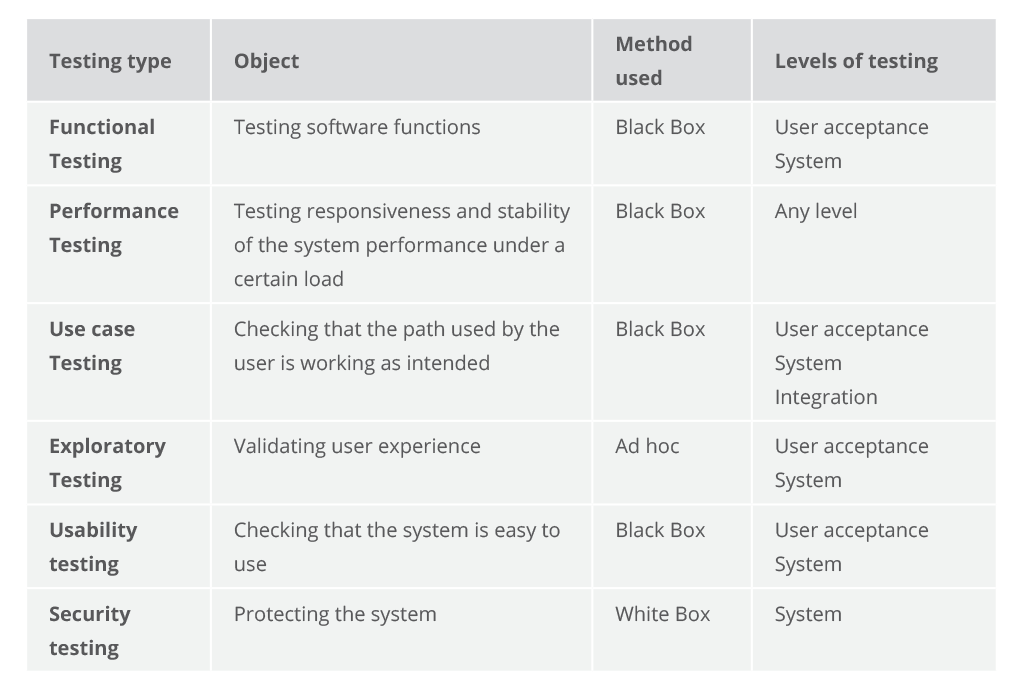
Most popular software testing types described co-ordinate to their object, method applied and testing levels during which they are used
- Functional Testing
Winning 83 per centum of the respondents' votes, functional testing is the most important testing type. This is to exist expected, since without functionality there would exist no use of all other non-functional aspects of the system.
In functional testing, the organisation is tested against the functional requirements by feeding it input and examining the output. This blazon of testing applies the black box method. Consequently, it gives significance not to the processing itself, only rather, on its results. Functional testing is normally performed inside the levels of system and acceptance.
Typically, the process of functional testing comprises the following set of deportment:
1. Outlines the functions for the software to perform
2. Composes the input data depending on function specifications
3. Determines the output depending on role specifications
4. Executes the exam case
five. Juxtaposes the received and expected outputs
- Performance Testing
Performance testing has been selected by 60.7 percent of respondents every bit the most important not-functional testing type. Performance testing is aimed at investigating the responsiveness and stability of the system operation under a certain load.
Depending on the workload, a organisation behavior is evaluated by dissimilar kinds of performance testing:
- Load Testing — at continuously increasing workload
- Stress Testing — at or beyond the limits of the anticipated workload
- Endurance Testing — at continuous and significant workload
- Fasten Testing — at suddenly and substantially increased workload
- Utilize Case Testing
Information technology'southward the most widely used testing technique, followed past exploratory testing. Use example describes how a organization will respond to a given scenario created past the user. Information technology is user-oriented and focuses on the actions and the actor, not taking into account the organisation input and output. Keeping the projection concepts in mind, developers write employ cases and after completing them, the behavior of the organisation is tested appropriately. Testers, in their turn, utilize them to create test cases.
Utilize case testing is applied widely in developing tests at organization or credence levels. It as well helps uncover the defects in integration testing. Apply case testing checks whether the path used by the user is working as intended and makes certain the tasks can be accomplished successfully. Applying use case testing, analysts can detect shortcomings and change the arrangement so that information technology attains efficiency and accuracy.
- Exploratory Testing
The exploratory testing technique was beginning described past Cem Kaner, a software engineering professor and consumer abet, every bit "a mode of software testing that emphasizes the personal freedom and responsibility of the individual tester to continually optimize the value of her work past treating exam-related learning, test design, exam execution, and test result interpretation every bit mutually supportive activities that run in parallel throughout the project."
Using the advertizing hoc method, exploratory testing does non rely on predefined and documented examination cases and test steps as most testing types do. Instead, it is an interactive and gratuitous-form process, with the principal focus on validating user feel, not code. Information technology has much in common with the advert hoc or intuitive testing but is more systematic. Applying exploratory testing, skilled testers tin can provide valuable and auditable results.
- Usability Testing
Chosen by 44.1 percentage of respondents, usability testing is performed from the end user's perspective to come across if the arrangement is piece of cake to employ. This testing type is not to be confused with user acceptance testing. The latter verifies that the final production meets the set requirements; the old ensures that the implementation approach will work for the user.
8. Test Automation
To speed up and improve the quality of software testing and improve its quality, it's important to adopt advanced automation.
Test automation is critical in terms of continuous testing equally it eases the brunt of managing all of the testing needs, allowing more time and attempt to exist spent on creating constructive test cases. The test automation trend is supported by the always-growing adoption of agile methodologies, which promote both test automation and continuous integration practices every bit the cornerstone of constructive software development. Nosotros invite you to check our commodity that compares the most popular automated testing tools including Selenium, TestComplete, and Ranorex.
The procedure of test automation is typically conducted in several consecutive steps:
- Preliminary Project Analysis
- Framework Engineering
- Test Cases Development
- Examination Cases Implementation
- Iterative Framework Support
Benefits of exam automation. Automation can be practical to virtually every testing type, at every level. As a result, the automation minimizes the human endeavor required to efficiently run tests, reduces time-to-marketplace and the cost of errors because the tests are performed up to 10 times faster when compared to manual testing process. Moreover, such a testing approach is more efficient as the framework covers over xc percent of the code, unveiling the issues that might not be visible in manual testing and can exist scaled as the product grows.
Test automation in numbers. Co-ordinate to the ISTQB® survey, 64.4 percent of their respondents vote for exam automation activities as the principal improvement expanse in software testing. At the same time, 43,4 pct of the respondents proper noun examination automation the pinnacle claiming in Active projects. Here are the almost striking problems faced in applying test automation based on the survey past Katalon Studio.

Examination automation challenges according to the Katalon Studio survey
The gradual growth of the contribution of test automation is confirmed by the following survey.
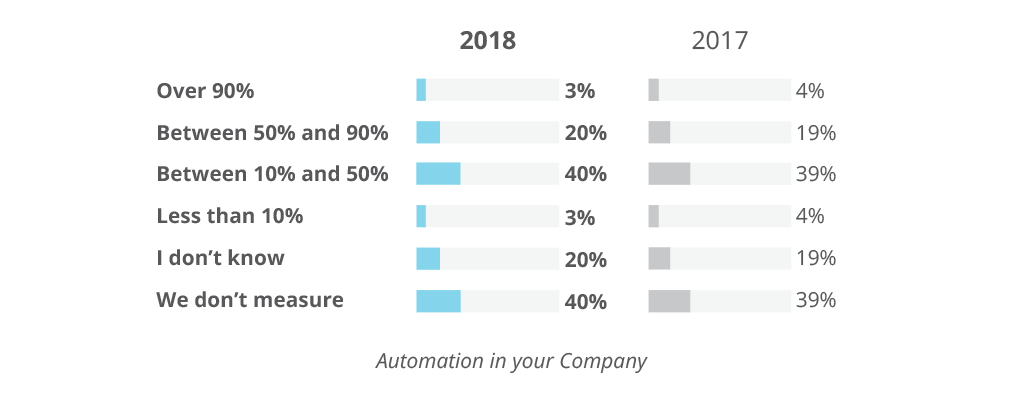
Epitome credit: State OF TESTING REPORT 2022
Automated exam activities include exam execution, functional exam example design, examination data generation, and testing of end-to-end business scenarios.
However, the near effective testing approaches combine manual and automated testing activities in order to achieve the best results.
nine. Regression Testing
Regression testing is the practice of verifying software beliefs after updates to ensure that the changes oasis't impacted existing system functions, stability, and overall integrity. Regression testing tin be practical to all levels and with all types of testing procedures only the most common style is to run regression testing according to use cases. Regression quality assurance workflow can be automatic to avert repetitive manual tests afterwards each update. There are multiple regression testing techniques:
- Retesting all test cases
- Selecting specific test cases
- Prioritizing test cases to verify the near critical ones first and and then examination the rest
- Hybrid techniques
10. The Future of Testing
Every bit a part of technological progress, testing is continually evolving to meet always-changing business organization needs as information technology adopts new tools that let the tester to push the boundaries of quality assurance.
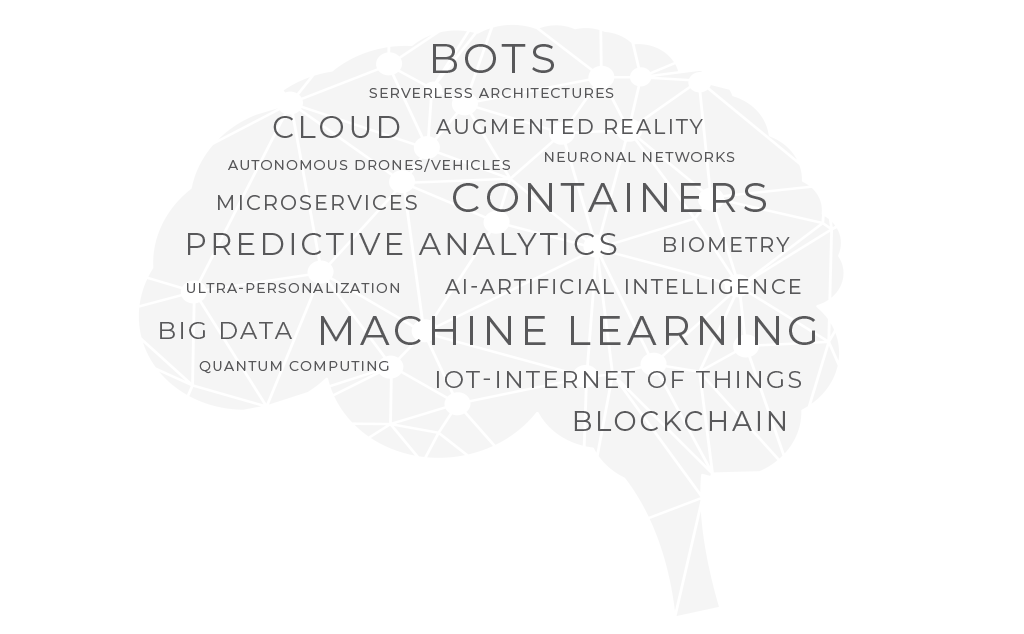 "Hot topics" in software testing in the coming years co-ordinate to the PractiTest survey
"Hot topics" in software testing in the coming years co-ordinate to the PractiTest survey
New subjects expected to affect software testing in near futurity are security, artificial intelligence, and big data.
- Security
The World Quality Report survey shows that security is ane of the most important elements of an IT strategy. Input from security is vital to protecting the business. Security vulnerabilities can seriously tarnish brand reputation. For those reasons, test environments and exam data are considered the master challenges in QA testing today.
Information protection and privacy laws as well enhance concerns nigh the security of test environments. If an environment contains personal test data and suffers a security breach, businesses must notify the regime immediately. Every bit a result, it is and then of import for test environments to be able to detect information breaches.
Almost popular in cloud environments, security testing intends to uncover system vulnerabilities and determine how well it can protect itself from unauthorized access, hacking, whatever code damage, etc. While dealing with the code of application, security testing refers to the white box testing method.
The four main focus areas in security testing:
- Network security
- Organization software security
- Client-side application security
- Server-side awarding security
It is highly recommended that security testing is included equally part of the standard software development process.
- Artificial Intelligence
The challenges of testing are increasing and their solutions have unlimited number of situations requiring artificial intelligence to examination them thoroughly. Different implementations of AI using car learning-based algorithms will shortly become embedded in applications to perform tasks once reserved for humans.
Although test automation solutions in the intelligence area are not well-established nonetheless, the shift towards more intelligence in testing is inevitable. Cognitive automation, machine learning, self-remediation, and predictive analysis are promising emerging techniques for the hereafter of test automation.
That said, a Boston-based startup mabl already simplifies functional testing by combining information technology with machine learning. "As we met with hundreds of software teams, nosotros latched on to this idea that developing… is very fast now, but in that location's a bottleneck in QA," says Izzy Azerbaijani, a co-founder of mabl. "Every fourth dimension you make a alter to your product, you take to test this change or build test automation."
With mabl there is no demand to write extensive tests by hand. Instead, y'all show the awarding the workflow you want to exam and the service performs those tests. Mabl can fifty-fifty automatically conform to small user interface changes and alert developers to whatsoever visual changes, JavaScript errors, broken links, and increased load times.
Adopting smarter automation solutions will be essential for testing the emerging intelligent applications and products in their rapidly changing business organisation environments.
- Big Data
Currently, the 2 major concerns regarding test data management are data compliance and big data.
First, with many onerous protection laws arriving on the scene, simply copying real-world data presents a risk of violating them. For case, the Eu's Full general Information Protection Regulation (GDRP) became constabulary in May 2022 for all companies operating in the European union. Given the threat of significant fines, information compliance concerns are on the front burner of most It departments today.
2nd, managing huge volumes of data that are constantly uploaded on various platforms demands a unique approach for testing as traditional techniques tin no longer cope.
Big information testing is aimed at checking the quality of information and verifying data processing. Data quality check involves various characteristics similar conformity, accuracy, duplication, consistency, validity, information completeness, etc. Data processing verification comprises performance and functional testing. Big data testing demands a loftier level of testing skills as the processing is very fast.
Conclusion
In 2022, Knight Upper-case letter Americas, a global financial firm, experienced an error in its automatic routing system for equity orders – the team deployed untested software to a production environment. As a event, the company lost over $460 million in only 45 minutes, which basically led to its bankruptcy.
History knows many more examples of software incidents which caused similar damage. Withal, testing remains one of the most disputed topics in software evolution. Many product owners doubt its value as a separate process, putting their businesses and products at stake while trying to save an actress penny.
Despite a widespread misbelief that a tester'south only job is to find bugs, testing and QA have a greater impact on the last product success. Having a deep understanding of the customer's concern and the product itself, QA engineers add value to the software and ensure its excellent quality. Moreover, applying their extensive knowledge of the production, testers tin bring value to the customer through additional services, similar tips, guidelines, and product use manuals. This results in reduced price of ownership and improved business efficiency.
References
- Software Quality – http://softwaretestingfundamentals.com/software-quality/
- The Three Aspects of Software Quality – http://world wide web.davidchappell.com/writing/white_papers/The_Three_Aspects_of_Software_Quality_v1.0-Chappell.pdf
- Foundations of Software Testing: ISTQB Certification – https://www.amazon.com/Foundations-Software-Testing-ISTQB-Certification/dp/1844809897
- Software Engineering: A Practitioner's Approach – https://www.amazon.com/Software-Engineering-Practitioners-Roger-Pressman/dp/0073375977/
- Examination Strategy – http://www.satisfice.com/presentations/strategy.pdf
- Test Strategy and Test Plan – http://www.testingexcellence.com/test-strategy-and-test-plan/
- IEEE Standard for Software and System Test Documentation 2008 – https://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/829-2008.html
- ISTQB Worldwide Software Testing Practices REPORT 2022-eighteen – https://www.istqb.org/documents/ISTQB%202017-18_Revised.pdf
- Defining Exploratory Testing – http://kaner.com/?p=46
- Evaluating Leave Criteria and Reporting – http://world wide web.softwaretestingmentor.com/evaluating-leave-criteria-and-reporting-in-testing-process/
- Myths and realities of iterative testing – http://test.techwell.com/sites/default/files/articles/XUS16337350file1_0.pdf
- Securities Exchange Act of 1934 – https://www.sec.gov/litigation/admin/2013/34-70694.pdf
- Globe Quality Report 2022-eighteen | Ninth Edition – https://www.sogeti.com/globalassets/global/downloads/testing/wqr-2017-2018/wqr_2017_v9_secure.pdf
- The virtually striking problems in exam automation: A survey May 2022 – https://d1h3p5fzmizjvp.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/05101901/The-Nigh-Striking-Problemns-in-Test-Automation-A-Survey.pdf
- State of testing report – http://qablog.practitest.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/2018_state_of_testing_report_1.2.pdf?full_name=Ksenia&email=annabond1995%40gmail.com&utm_source=qablog&utm_medium=push&utm_campaign=&utm_term=&utm_content=download&page_type=resources%2C&role=Other&industry=Marketing%2C%20advertising%20and%20media&referrer=
- DevOps Testing Tutorial: How DevOps will Impact QA Testing? – https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/devops-and-software-testing/
Source: https://www.altexsoft.com/whitepapers/quality-assurance-quality-control-and-testing-the-basics-of-software-quality-management/
Posted by: anthonymadmon.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can Statit Qc Software Be Used On Aircraft Repair"
Post a Comment